Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Continuity
Problem 2.2.7
Textbook Question
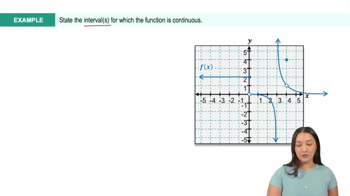
Textbook QuestionDetermine the points on the interval (0, 5) at which the following functions f have discontinuities. At each point of discontinuity, state the conditions in the continuity checklist that are violated. <IMAGE>
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Continuity of Functions
A function is continuous at a point if three conditions are met: the function is defined at that point, the limit of the function as it approaches that point exists, and the limit equals the function's value at that point. Understanding these conditions is crucial for identifying points of discontinuity.
Recommended video:

Intro to Continuity
Types of Discontinuities
Discontinuities can be classified into three main types: removable, jump, and infinite. A removable discontinuity occurs when a function can be made continuous by redefining a point, a jump discontinuity involves a sudden change in function value, and an infinite discontinuity occurs when the function approaches infinity at a point.
Recommended video:

Determine Continuity Algebraically
The Limit Concept
The limit of a function describes the behavior of the function as it approaches a specific point. If the left-hand limit and right-hand limit at a point do not match, or if either limit does not exist, the function is discontinuous at that point. This concept is fundamental in analyzing continuity.
Recommended video:

One-Sided Limits
Related Videos
Related Practice