Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
4. Applications of Derivatives
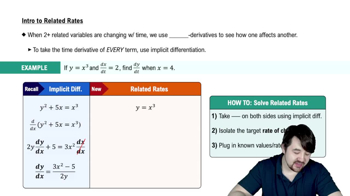
Related Rates
Problem 34
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDemand and elasticity The economic advisor of a large tire store proposes the demand function D(p) = 1800/p-40, where D(p) is the number of tires of one brand and size that can be sold in one day at a price p.
c. Find the elasticity function on the domain of the demand function.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Demand Function
A demand function expresses the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded by consumers. In this case, D(p) = 1800/p - 40 indicates how the number of tires sold changes as the price p varies. Understanding this function is crucial for analyzing how price affects consumer behavior in the market.
Recommended video:

Properties of Functions
Elasticity of Demand
Elasticity of demand measures how responsive the quantity demanded is to a change in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. This concept helps determine whether demand is elastic (sensitive to price changes) or inelastic (less sensitive), which is essential for pricing strategies.
Recommended video:
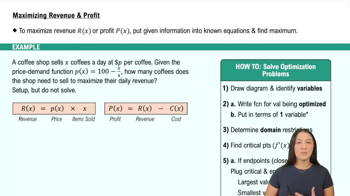
Maximizing Profit & Revenue
Calculating Elasticity
To find the elasticity function, we use the formula E(p) = (D'(p) * p) / D(p), where D'(p) is the derivative of the demand function with respect to price. This calculation provides a function that describes how elasticity varies with price, allowing for a deeper understanding of consumer sensitivity to price changes across different price levels.
Recommended video:

Determining Error and Relative Error Example 1
Related Videos
Related Practice