Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits
Problem 4f
Textbook Question
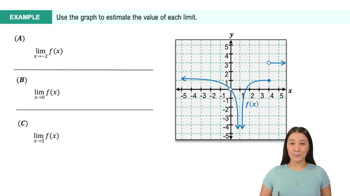
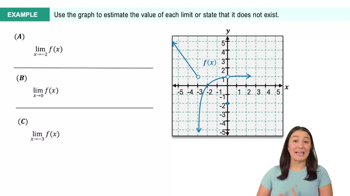
Textbook QuestionUse the graph of f in the figure to evaluate the function or analyze the limit. <IMAGE>
lim x→1 f(x)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Limits
A limit is a fundamental concept in calculus that describes the behavior of a function as its input approaches a certain value. It helps in understanding how functions behave near specific points, even if they are not defined at those points. Evaluating limits is crucial for determining continuity, derivatives, and integrals.
Recommended video:

One-Sided Limits
Continuity
A function is continuous at a point if the limit of the function as it approaches that point equals the function's value at that point. Continuity ensures that there are no breaks, jumps, or holes in the graph of the function, which is essential for evaluating limits and understanding the overall behavior of the function.
Recommended video:

Intro to Continuity
Graphical Analysis
Graphical analysis involves interpreting the visual representation of a function to understand its properties, such as limits, continuity, and behavior at specific points. By examining the graph, one can often determine the limit of a function as it approaches a certain value, which is particularly useful when the function is not easily evaluated algebraically.
Recommended video:

Derivatives Applied To Velocity

 6:47m
6:47mWatch next
Master Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning