- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals3h 25m
5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives
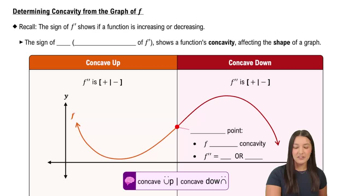
Concavity
Multiple Choice
Determine the intervals for which the function is concave up or concave down. State the inflection points.
f(x)=2sinx+3x; 0 < x < 2π
A
Concave down: (0,π); concave up: (π,2π); Inflection pt: (π,3π)
B
Concave down: (0,π); concave up: (π,2π); Inflection pt: (π,2+3π)
C
Concave down: (0,2π), (π,23π); concave up: (2π,π), (23π,2π); Inflection pts: (2π,24+3π), (π,3π), (23π,2−4+9π)
D
Concave up: (0,2π); No inflection pt

 6:38m
6:38mWatch next
Master Determining Concavity from the Graph of f with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice