Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
0. Functions
Transformations
Problem 54a
Textbook Question
Describe how each graph is obtained from the graph of 𝔂 = ƒ(x).
a. 𝔂 = ƒ(x - 5)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start with the graph of the function 𝔂 = ƒ(x). This is your base graph.
Identify the transformation applied to the function. In this case, the transformation is 𝔂 = ƒ(x - 5).
Recognize that the expression (x - 5) inside the function indicates a horizontal shift. Specifically, it is a shift to the right.
To apply this transformation, take each point (x, y) on the original graph of 𝔂 = ƒ(x) and move it 5 units to the right. This means you will replace each x-coordinate with (x + 5).
Plot the new points to obtain the graph of 𝔂 = ƒ(x - 5). The shape of the graph remains unchanged, but its position is shifted 5 units to the right.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Transformation
Function transformation refers to the process of altering the graph of a function through shifts, stretches, or reflections. These transformations can change the position and shape of the graph without altering its fundamental properties. Understanding how to manipulate the function's equation allows one to predict how the graph will change.
Recommended video:
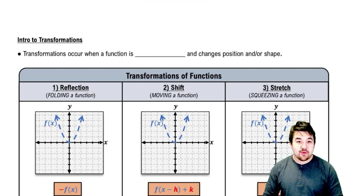
Intro to Transformations
Horizontal Shifts
A horizontal shift occurs when the graph of a function is moved left or right along the x-axis. For the function 𝔶 = ƒ(x - 5), the graph is shifted 5 units to the right. This transformation is achieved by replacing x with (x - c), where c is the number of units shifted, affecting the input values of the function.
Recommended video:

Intro to Transformations
Graphing Functions
Graphing functions involves plotting points that represent the output of a function for various input values. Understanding how to graph functions is essential for visualizing transformations. By knowing the original graph of 𝔶 = ƒ(x), one can easily apply transformations to see how the graph changes, enhancing comprehension of function behavior.
Recommended video:

Graph of Sine and Cosine Function

 5:25m
5:25mWatch next
Master Intro to Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

