Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
0. Functions
Combining Functions
Problem 39a
Textbook Question
Composition of Functions
In Exercises 39 and 40, find
a. (ƒ ○ g) (-1).
ƒ(x) = 1/x , g(x) = 1/√ x + 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the composition of functions: The composition (ƒ ○ g)(x) means applying g first and then applying ƒ to the result of g(x).
Substitute x = -1 into the function g(x): g(-1) = 1/√(-1 + 2). Calculate the expression inside the square root first.
Simplify the expression inside g(-1): √(-1 + 2) = √1 = 1. Therefore, g(-1) = 1/1 = 1.
Now apply the function ƒ to the result of g(-1): ƒ(g(-1)) = ƒ(1). Substitute 1 into ƒ(x) = 1/x.
Simplify ƒ(1): ƒ(1) = 1/1 = 1. Therefore, (ƒ ○ g)(-1) = 1.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Composition
Function composition involves combining two functions to create a new function. The notation (ƒ ○ g)(x) means to apply function g first and then apply function f to the result of g. This is essential for solving the problem, as it requires evaluating g at a specific input and then using that output as the input for f.
Recommended video:

Evaluate Composite Functions - Special Cases
Evaluating Functions
Evaluating a function means substituting a specific value into the function's formula to find the output. In this case, we need to evaluate g at -1, which requires substituting -1 into the function g(x) = 1/√(x + 2). Understanding how to correctly substitute values is crucial for finding the correct outputs in function composition.
Recommended video:
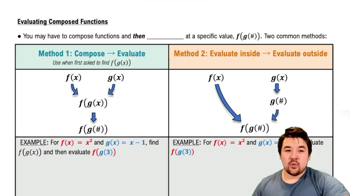
Evaluating Composed Functions
Domain of Functions
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values for which the function is defined. For the given functions, we must consider the domains of both f(x) = 1/x and g(x) = 1/√(x + 2) to ensure that the inputs do not lead to undefined expressions, such as division by zero or taking the square root of a negative number.
Recommended video:
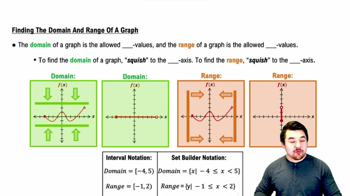
Finding the Domain and Range of a Graph

 5:56m
5:56mWatch next
Master Adding & Subtracting Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learning