- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals3h 25m
0. Functions
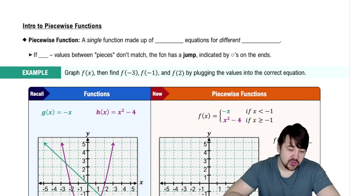
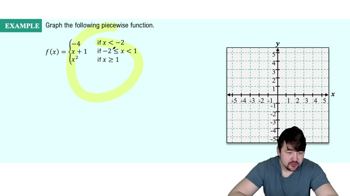
Piecewise Functions
Problem 1.36
Textbook Question
In Exercises 35 and 36, find the (a) domain and (b) range.
𝔂 = { -x - 2, -2 ≤ x ≤ - 1
{ x, -1 < x ≤ 1
{ -x + 2, 1 < x ≤ 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the domain of the piecewise function. The domain is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For this piecewise function, the domain is given by the intervals: -2 ≤ x ≤ -1, -1 < x ≤ 1, and 1 < x ≤ 2. Therefore, the domain is the union of these intervals: [-2, 2].
Step 2: Determine the range of the first piece of the function, y = -x - 2, for the interval -2 ≤ x ≤ -1. Calculate the values of y at the endpoints of the interval: when x = -2, y = -(-2) - 2 = 0; when x = -1, y = -(-1) - 2 = -1. Thus, the range for this piece is [-1, 0].
Step 3: Determine the range of the second piece of the function, y = x, for the interval -1 < x ≤ 1. Calculate the values of y at the endpoints of the interval: when x approaches -1 from the right, y approaches -1; when x = 1, y = 1. Thus, the range for this piece is (-1, 1].
Step 4: Determine the range of the third piece of the function, y = -x + 2, for the interval 1 < x ≤ 2. Calculate the values of y at the endpoints of the interval: when x approaches 1 from the right, y approaches 1; when x = 2, y = -2 + 2 = 0. Thus, the range for this piece is (0, 1].
Step 5: Combine the ranges from each piece of the function to find the overall range. The ranges from the three pieces are [-1, 0], (-1, 1], and (0, 1]. The overall range is the union of these intervals, which is [-1, 1].
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
7mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Related Videos
Related Practice