Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Transformations
Problem 55b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionUse shifts and scalings to transform the graph of into the graph of g. Use a graphing utility to check your work.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
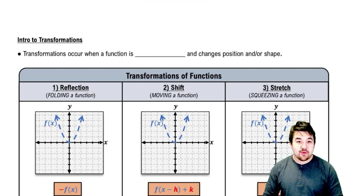
Function Transformation
Function transformation involves altering the graph of a function through shifts, stretches, and reflections. In this case, the function f(x) = x² is transformed into g(x) = f(2x - 4) by applying horizontal and vertical shifts and scalings. Understanding how these transformations affect the graph is crucial for accurately sketching the new function.
Recommended video:
Intro to Transformations
Horizontal Shifts
Horizontal shifts occur when the input of a function is adjusted by adding or subtracting a constant. For g(x) = f(2x - 4), the term '−4' indicates a shift to the right by 4 units. This concept is essential for determining how the graph of the original function moves along the x-axis.
Recommended video:

Intro to Transformations
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling refers to stretching or compressing the graph of a function by multiplying the input by a constant factor. In g(x) = f(2x - 4), the '2' in front of x indicates a horizontal compression by a factor of 1/2. This concept helps in understanding how the shape of the graph changes in relation to the original function.
Recommended video:
Relations & Functions Example 1

 5:25m
5:25mWatch next
Master Intro to Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

