Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals3h 25m
2. Intro to Derivatives
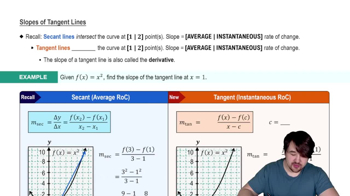
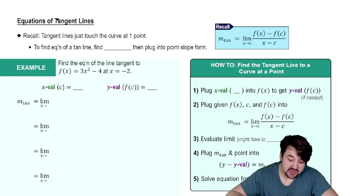
Tangent Lines and Derivatives
Problem 97
Textbook Question
97–100. Logistic growth Scientists often use the logistic growth function P(t) = P₀K / P₀+(K−P₀)e^−r₀t to model population growth, where P₀ is the initial population at time t=0, K is the carrying capacity, and r₀ is the base growth rate. The carrying capacity is a theoretical upper bound on the total population that the surrounding environment can support. The figure shows the sigmoid (S-shaped) curve associated with a typical logistic model. <IMAGE>
{Use of Tech} Gone fishing When a reservoir is created by a new dam, 50 fish are introduced into the reservoir, which has an estimated carrying capacity of 8000 fish. A logistic model of the fish population is P(t) = 400,000 / 50+7950e^−0.5t, where t is measured in years.
a. Graph P using a graphing utility. Experiment with different windows until you produce an S-shaped curve characteristic of the logistic model. What window works well for this function?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the parameters in the logistic growth function P(t) = 400,000 / (50 + 7950e^(-0.5t)), where P₀ = 50, K = 8000, and r₀ = 0.5.
Set up a graphing utility, such as Desmos or a graphing calculator, to input the logistic function P(t).
Choose an appropriate window for the graph. A good starting point for the x-axis (time t) could be from 0 to 20 years, and for the y-axis (population P), from 0 to 8000 fish, since this is the carrying capacity.
Plot the function and observe the shape of the curve. Adjust the window settings if necessary to better visualize the S-shaped curve characteristic of logistic growth.
Experiment with different values for the x-axis and y-axis limits to find the best view of the curve, ensuring that the population approaches the carrying capacity as time increases.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?

 5:13m
5:13mWatch next
Master Slopes of Tangent Lines with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice