Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals3h 25m
0. Functions
Introduction to Functions
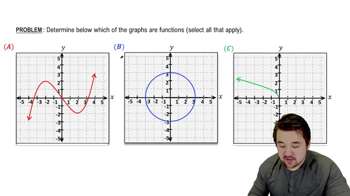
Problem 1.28
Textbook Question
In Exercises 19–32, find the (a) domain and (b) range.
_____
𝔂 = -1 + ∛ 2 - x
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the function type. The given function is 𝑦 = -1 + ∛(2 - x), which involves a cube root. Cube root functions are defined for all real numbers, so there are no restrictions on the domain.
Step 2: Determine the domain. Since the cube root function is defined for all real numbers, the domain of 𝑦 = -1 + ∛(2 - x) is all real numbers, or (-∞, ∞).
Step 3: Analyze the range of the function. The cube root function, ∛(x), can take any real number as its output, ranging from -∞ to ∞.
Step 4: Consider the transformations applied to the cube root function. The function 𝑦 = -1 + ∛(2 - x) involves a vertical shift downward by 1 unit. This does not affect the range of the cube root function, which remains all real numbers.
Step 5: Conclude the range. Since the cube root function can output any real number and the vertical shift does not restrict this, the range of the function is also all real numbers, or (-∞, ∞).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Domain
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For the given function 𝔂 = -1 + ∛(2 - x), we need to determine the values of x that do not lead to undefined expressions. Since the cube root function is defined for all real numbers, the domain is all real numbers where 2 - x is a real number, which translates to x being less than or equal to 2.
Recommended video:
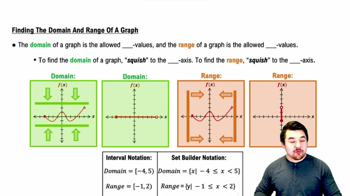
Finding the Domain and Range of a Graph
Range
The range of a function is the set of all possible output values (y-values) that the function can produce. In the case of 𝔂 = -1 + ∛(2 - x), as x approaches negative infinity, the cube root term will also approach negative infinity, and as x approaches 2, the output approaches -1. Therefore, the range of this function is all real numbers greater than or equal to -1.
Recommended video:

Finding the Domain and Range of a Graph
Cube Root Function
The cube root function, denoted as ∛x, is a function that returns the number which, when cubed, gives the input x. This function is defined for all real numbers, meaning it can take any real number as input and will produce a real number as output. Understanding the properties of the cube root function is essential for analyzing the behavior of the given function, particularly in determining its domain and range.
Recommended video:

Graphs of Common Functions

 1:36m
1:36mWatch next
Master Introduction to Calculus Channel with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning