Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
0. Functions
Introduction to Functions
Problem 1.10
Textbook Question
Let ƒ(x) = 1/ (x³+1).
Compute ƒ(2) and ƒ(y²).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the function given: \( f(x) = \frac{1}{x^3 + 1} \).
To compute \( f(2) \), substitute \( x = 2 \) into the function: \( f(2) = \frac{1}{2^3 + 1} \).
Simplify the expression for \( f(2) \): calculate \( 2^3 \) and add 1.
To compute \( f(y^2) \), substitute \( x = y^2 \) into the function: \( f(y^2) = \frac{1}{(y^2)^3 + 1} \).
Simplify the expression for \( f(y^2) \): calculate \( (y^2)^3 \) and add 1.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Evaluation
Function evaluation involves substituting a specific value into a function to determine its output. For example, to compute ƒ(2) for the function ƒ(x) = 1/(x³ + 1), you replace x with 2, resulting in ƒ(2) = 1/(2³ + 1) = 1/9.
Recommended video:
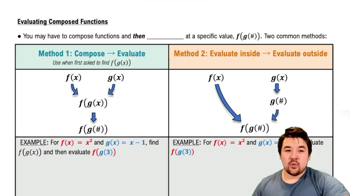
Evaluating Composed Functions
Polynomial Functions
A polynomial function is a mathematical expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients. In the function ƒ(x) = 1/(x³ + 1), the denominator x³ + 1 is a polynomial of degree three, which influences the behavior and properties of the function.
Recommended video:
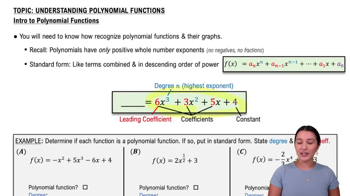
Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Substitution in Functions
Substitution in functions refers to replacing a variable with another expression or value. In this case, computing ƒ(y²) means substituting y² into the function, leading to ƒ(y²) = 1/((y²)³ + 1) = 1/(y^6 + 1), which allows for further analysis of the function's behavior based on the variable y.
Recommended video:

Finding Limits by Direct Substitution

 1:36m
1:36mWatch next
Master Introduction to Calculus Channel with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning