Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits
Problem 2.4.68a
Textbook Question
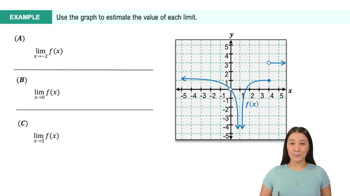
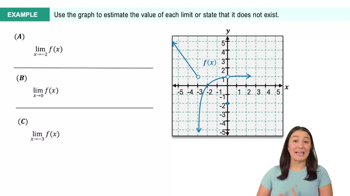
Textbook QuestionGiven the graph of f in the following figures, find the slope of the secant line that passes through (0,0) and (h,f(h))in terms of h, for h>0 and h<0.
f(x)=x1/3 <IMAGE>
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Secant Line
A secant line is a straight line that intersects a curve at two or more points. In calculus, it is often used to approximate the slope of the curve between those points. The slope of the secant line can be calculated using the formula (f(b) - f(a)) / (b - a), where a and b are the x-coordinates of the points on the curve.
Recommended video:
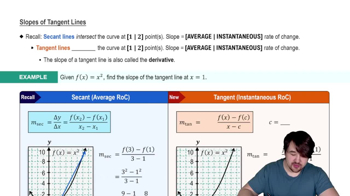
Slopes of Tangent Lines
Slope of a Function
The slope of a function at a given point represents the rate of change of the function's value with respect to changes in its input. For a secant line, the slope is determined by the difference in the function's values at two points divided by the difference in their x-coordinates. This concept is foundational for understanding derivatives, which represent instantaneous rates of change.
Recommended video:
Guided course
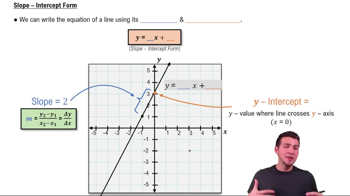
Slope-Intercept Form
Cube Root Function
The cube root function, denoted as f(x) = x^(1/3), is a mathematical function that returns the number whose cube is x. This function is defined for all real numbers and has a characteristic shape, being continuous and increasing. Understanding its behavior, especially near the origin, is crucial for analyzing the secant line's slope as h approaches zero from both positive and negative directions.
Recommended video:

Graphs of Common Functions

 6:47m
6:47mWatch next
Master Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning