Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Definite Integral
The area function A(x) represents the definite integral of the function f(t) from t=0 to t=x. This integral calculates the net area between the curve and the t-axis, accounting for regions above and below the axis. Understanding how to evaluate definite integrals is crucial for finding specific area values, such as A(2) in this case.
Recommended video:
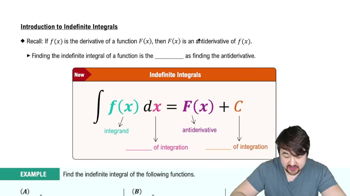
Introduction to Indefinite Integrals
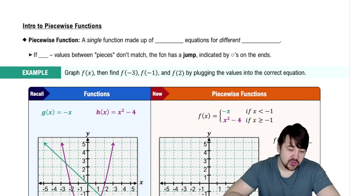
Piecewise Functions
The function f(t) is defined piecewise, meaning it has different expressions based on the value of t. For t ≤ 3, f(t) = -2t + 8, and for t > 3, f(t) = 2. Recognizing how to work with piecewise functions is essential for correctly evaluating the integral over the specified interval, as the function's behavior changes at t=3.
Recommended video:
Area Under a Curve
The area under a curve can be interpreted as the integral of the function over a given interval. In this problem, calculating A(2) involves finding the area under f(t) from t=0 to t=2. This requires integrating the appropriate expression of f(t) over the specified limits, which is fundamental in applications of calculus to determine physical quantities like area.
Recommended video:
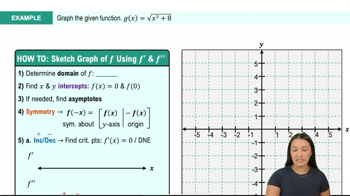
Summary of Curve Sketching Example 2
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution