Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
3. Techniques of Differentiation
Basic Rules of Differentiation
Problem 3.43c
Textbook Question
City urbanization City planners model the size of their city using the function A(t) = - 1/50t² + 2t +20, for 0 ≤ t ≤ 50, where A is measured in square miles and t is the number of years after 2010.
c. Suppose the population density of the city remains constant from year to year at 1000 people mi². Determine the growth rate of the population in 2030.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the function that models the size of the city. The function given is A(t) = -\frac{1}{50}t^2 + 2t + 20, where A is the area in square miles and t is the number of years after 2010.
Step 2: Determine the year 2030 in terms of t. Since t is the number of years after 2010, for the year 2030, t = 2030 - 2010 = 20.
Step 3: Find the derivative of A(t) with respect to t to determine the rate of change of the area. The derivative, A'(t), represents the growth rate of the city's area in square miles per year.
Step 4: Calculate A'(t) by differentiating A(t). A'(t) = \frac{d}{dt}(-\frac{1}{50}t^2 + 2t + 20) = -\frac{1}{25}t + 2.
Step 5: Evaluate A'(t) at t = 20 to find the growth rate of the city's area in 2030. Then, multiply this rate by the population density (1000 people/mi²) to find the growth rate of the population.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Analysis
Understanding the function A(t) = -1/50t² + 2t + 20 is crucial for analyzing the area of the city over time. This quadratic function represents a parabolic curve, where the coefficients indicate how the area changes with respect to time. The vertex of the parabola will provide insights into the maximum area, while evaluating the function at specific values of t will yield the area at those years.
Recommended video:

Derivatives Applied To Velocity
Population Density
Population density is defined as the number of people per unit area, in this case, 1000 people per square mile. This constant density allows us to calculate the total population by multiplying the area of the city A(t) by the density. Understanding this relationship is essential for determining how the population grows as the area of the city changes over time.
Recommended video:

The Quotient Rule Example 5
Rate of Change
The growth rate of the population can be determined by finding the derivative of the area function A(t) with respect to time t. This derivative, A'(t), gives the instantaneous rate of change of the area, which, when multiplied by the constant population density, will yield the growth rate of the population. Evaluating this derivative at t = 20 (for the year 2030) will provide the specific growth rate at that time.
Recommended video:
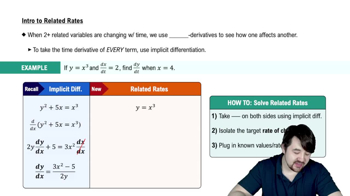
Intro To Related Rates

 3:59m
3:59mWatch next
Master Derivatives of Linear Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice