Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Combining Functions
Problem 88i
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionComposition of even and odd functions from tables Assume ƒ is an even function, g is an odd function, and both are defined at 0. Use the (incomplete) table to evaluate the given compositions. <IMAGE>
i. g(g(g(-1)))
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Even and Odd Functions
Even functions are symmetric about the y-axis, meaning that f(x) = f(-x) for all x in their domain. Odd functions, on the other hand, are symmetric about the origin, satisfying the condition g(x) = -g(-x). Understanding these properties is crucial for evaluating compositions of such functions, as they dictate how the function values behave under negation.
Recommended video:

Properties of Functions
Function Composition
Function composition involves applying one function to the result of another. If you have two functions f and g, the composition g(f(x)) means you first apply f to x, then apply g to the result. This concept is essential for evaluating expressions like g(g(g(-1))) as it requires sequentially substituting the output of one function into the next.
Recommended video:

Evaluate Composite Functions - Special Cases
Evaluating Functions at Specific Points
To evaluate a function at a specific point, you substitute that point into the function's expression. For example, to find g(-1), you would look up the value of g at -1 in the provided table. This step is necessary for calculating compositions, as each function's output becomes the input for the next function in the sequence.
Recommended video:
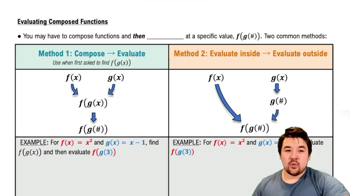
Evaluating Composed Functions

 5:56m
5:56mWatch next
Master Adding & Subtracting Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learning