Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
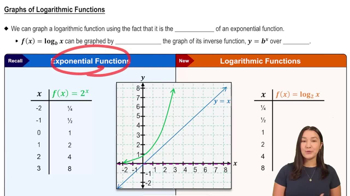
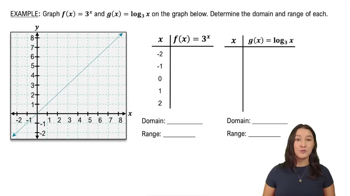
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Common Functions
Problem 17
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFind the linear function whose graph passes through the point (3, 2) and is parallel to the line .
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Linear Functions
A linear function is a mathematical expression that describes a straight line when graphed. It is typically represented in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. Understanding linear functions is crucial for determining the relationship between variables and for solving problems involving lines.
Recommended video:
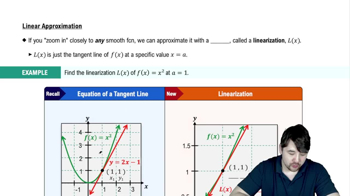
Linearization
Slope
The slope of a line measures its steepness and direction, calculated as the change in y divided by the change in x (rise over run). For two parallel lines, the slopes are equal. In this question, the slope of the given line y = 3x + 8 is 3, which will be the same for the linear function we need to find.
Recommended video:
Guided course
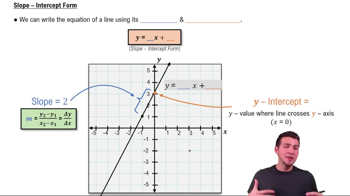
Slope-Intercept Form
Point-Slope Form
The point-slope form of a linear equation is expressed as y - y1 = m(x - x1), where (x1, y1) is a specific point on the line and m is the slope. This form is particularly useful for writing the equation of a line when you know a point on the line and its slope, allowing for straightforward calculations in this problem.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Slope-Intercept Form

 5:57m
5:57mWatch next
Master Graphs of Common Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice