Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits
Problem 2.5.64
Textbook Question
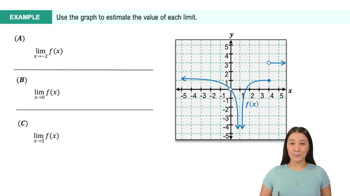
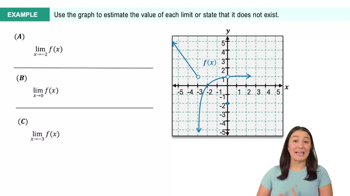
Textbook QuestionIf a function f represents a system that varies in time, the existence of lim means that the system reaches a steady state (or equilibrium). For the following systems, determine whether a steady state exists and give the steady-state value.
The population of a bacteria culture is given by .
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Limits
In calculus, a limit describes the behavior of a function as its input approaches a certain value. Specifically, the limit as t approaches infinity examines how the function behaves as time progresses indefinitely. Understanding limits is crucial for determining the long-term behavior of dynamic systems, such as whether they stabilize or diverge.
Recommended video:

One-Sided Limits
Steady State
A steady state in a system occurs when the variables of interest no longer change over time, indicating that the system has reached equilibrium. Mathematically, this is represented by the existence of a limit as time approaches infinity. In the context of the given function, identifying the steady-state value involves evaluating the limit of the population function as time increases.
Recommended video:
Intro to Continuity Example 1
Population Dynamics
Population dynamics is a field of study that examines how populations change over time due to various factors such as birth, death, and resource availability. The function provided, p(t) = 2500/(t+1), models the growth of a bacterial culture, illustrating how the population evolves and approaches a maximum capacity as time progresses. Understanding these dynamics is essential for analyzing the behavior of biological systems.
Recommended video:

The Quotient Rule Example 5

 6:47m
6:47mWatch next
Master Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning