Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits
Problem 2.31a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionA projectile is fired vertically upward and has a position given by s(t)=−16t^2+128t+192, for 0≤t≤9.
a. Graph the position function, for 0≤t≤9.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
8mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
The position function s(t) = -16t^2 + 128t + 192 is a quadratic function, characterized by its parabolic shape. Quadratic functions can be expressed in the standard form ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants. The coefficient 'a' determines the direction of the parabola (upward or downward), while 'b' and 'c' affect its position and vertex.
Recommended video:
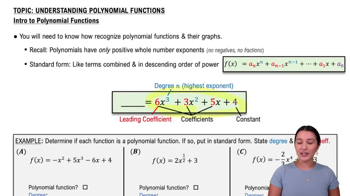
Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Graphing Techniques
Graphing a quadratic function involves identifying key features such as the vertex, axis of symmetry, and intercepts. The vertex can be found using the formula t = -b/(2a), which gives the time at which the projectile reaches its maximum height. The x-intercepts (roots) can be found using the quadratic formula, and the y-intercept is simply the value of s(0).
Recommended video:

Graphing The Derivative
Projectile Motion
Projectile motion describes the motion of an object under the influence of gravity, typically modeled by a quadratic function. In this case, the function s(t) represents the height of the projectile over time, with the negative coefficient indicating that gravity is acting downward. Understanding the principles of projectile motion helps in analyzing the behavior of the object, including its maximum height and time of flight.
Recommended video:

Derivatives Applied To Acceleration Example 2

 6:47m
6:47mWatch next
Master Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning