Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
0. Functions
Introduction to Functions
Problem 1.19
Textbook Question
In Exercises 19–32, find the (a) domain and (b) range.
𝔂 = |x| - 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the function type. The given function is 𝑦 = |𝑥| - 2, which is an absolute value function. Absolute value functions are defined for all real numbers.
Step 2: Determine the domain of the function. Since the absolute value function is defined for all real numbers, the domain of 𝑦 = |𝑥| - 2 is all real numbers, which can be expressed as (-∞, ∞).
Step 3: Analyze the transformation of the function. The function 𝑦 = |𝑥| - 2 is a vertical shift of the basic absolute value function 𝑦 = |𝑥|. The graph of 𝑦 = |𝑥| is shifted 2 units downward.
Step 4: Determine the range of the function. The basic absolute value function 𝑦 = |𝑥| has a range of [0, ∞). After shifting the graph 2 units downward, the range of 𝑦 = |𝑥| - 2 becomes [-2, ∞).
Step 5: Summarize the domain and range. The domain of the function 𝑦 = |𝑥| - 2 is all real numbers (-∞, ∞), and the range is [-2, ∞).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Domain
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For the function y = |x| - 2, the absolute value function |x| is defined for all real numbers, meaning the domain is all real numbers, or (-∞, ∞). Understanding the domain is crucial for determining the valid inputs for the function.
Recommended video:
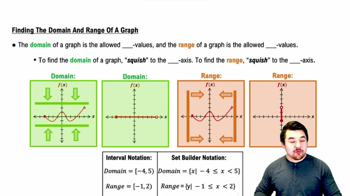
Finding the Domain and Range of a Graph
Range
The range of a function is the set of all possible output values (y-values) that the function can produce. In the case of y = |x| - 2, the minimum value occurs when |x| is zero, resulting in y = -2. As x increases or decreases, y increases without bound. Therefore, the range is [-2, ∞), indicating that y can take any value greater than or equal to -2.
Recommended video:

Finding the Domain and Range of a Graph
Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function, denoted as |x|, outputs the non-negative value of x regardless of its sign. This means |x| is always zero or positive. In the function y = |x| - 2, the absolute value affects the shape of the graph, creating a V-like structure that opens upwards, shifted down by 2 units. Understanding this function is essential for analyzing the overall behavior of the given equation.
Recommended video:

Average Value of a Function

 1:36m
1:36mWatch next
Master Introduction to Calculus Channel with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning