Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
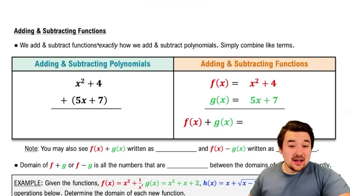
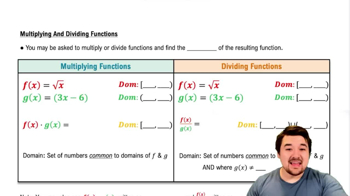
Combining Functions
Problem 88g
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionComposition of even and odd functions from tables Assume ƒ is an even function, g is an odd function, and both are defined at 0. Use the (incomplete) table to evaluate the given compositions. <IMAGE>
g. ƒ (g(g(-2)))
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Even and Odd Functions
An even function is defined by the property that f(x) = f(-x) for all x in its domain, meaning its graph is symmetric about the y-axis. An odd function satisfies g(x) = -g(-x), indicating that its graph is symmetric about the origin. Understanding these properties is crucial for evaluating compositions of functions, as they influence the output based on the input's sign.
Recommended video:

Properties of Functions
Function Composition
Function composition involves applying one function to the result of another, denoted as (f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)). In this case, we need to evaluate g(g(-2)) first, and then apply the even function f to that result. Mastery of function composition is essential for solving problems that require multiple function evaluations.
Recommended video:

Evaluate Composite Functions - Special Cases
Evaluating Functions at Specific Points
To evaluate functions at specific points, one must substitute the given input into the function's definition or table. For instance, to find g(-2), we look up the value of g at -2, and then use that result to find g(g(-2)). This step-by-step evaluation is critical for accurately determining the final output of the composed functions.
Recommended video:
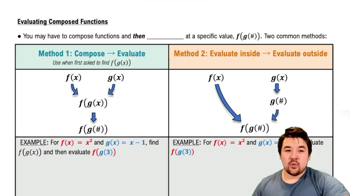
Evaluating Composed Functions

 5:56m
5:56mWatch next
Master Adding & Subtracting Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learning