- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals3h 25m
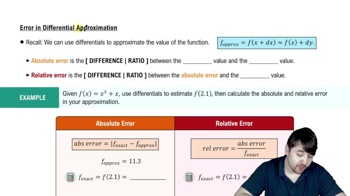
4. Applications of Derivatives
Differentials
Problem 7
Textbook Question
For each function ƒ and interval [a, b], a graph of ƒ is given along with the secant line that passes though the graph of ƒ at x = a and x = b.
a. Use the graph to make a conjecture about the value(s) of c satisfying the equation (ƒ(b) - ƒ(a)) / (b-a) = ƒ' (c) .
b. Verify your answer to part (a) by solving the equation (ƒ(b) - ƒ(a)) / (b-a) = ƒ' (c) for c.
ƒ(x) = x⁵/16 ; [-2, 2] <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the Mean Value Theorem (MVT), which states that for a continuous function ƒ on the closed interval [a, b] that is differentiable on the open interval (a, b), there exists at least one c in (a, b) such that (ƒ(b) - ƒ(a)) / (b-a) = ƒ'(c).
Step 2: Calculate ƒ(a) and ƒ(b) for the given function ƒ(x) = x^5/16 at the endpoints of the interval [a, b] = [-2, 2]. This involves substituting x = -2 and x = 2 into the function to find ƒ(-2) and ƒ(2).
Step 3: Compute the average rate of change of the function over the interval [-2, 2] using the formula (ƒ(b) - ƒ(a)) / (b-a). Substitute the values of ƒ(-2) and ƒ(2) obtained in Step 2 into this formula.
Step 4: Find the derivative of the function ƒ(x) = x^5/16, which is ƒ'(x) = (5/16)x^4. This derivative will be used to find the value of c that satisfies the MVT.
Step 5: Set the average rate of change from Step 3 equal to the derivative ƒ'(c) = (5/16)c^4 and solve for c. This involves equating the expression from Step 3 to (5/16)c^4 and solving the resulting equation for c to find the value(s) of c in the interval (-2, 2).
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?