Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Combining Functions
Problem 1.1.45
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWorking with composite functions Find possible choices for outer and inner functions ƒ and g such that the given function h equals ƒ o g .
h(x) = √ (x⁴ + 2 )
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
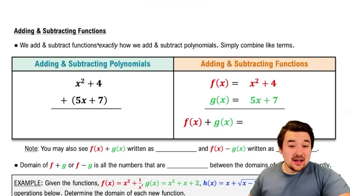
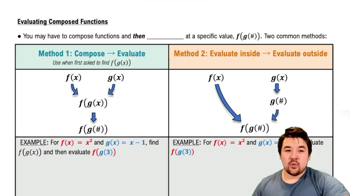
Composite Functions
A composite function is formed when one function is applied to the result of another function. It is denoted as (f o g)(x) = f(g(x)), where f is the outer function and g is the inner function. Understanding how to decompose a function into its components is essential for identifying suitable outer and inner functions that yield the desired composite function.
Recommended video:

Evaluate Composite Functions - Special Cases
Function Decomposition
Function decomposition involves breaking down a complex function into simpler constituent functions. This process is crucial when working with composite functions, as it allows us to identify potential candidates for the inner and outer functions. For example, in the function h(x) = √(x⁴ + 2), recognizing the structure of the expression can guide us in selecting appropriate f and g.
Recommended video:

Properties of Functions
Square Root Function
The square root function, denoted as √x, is a fundamental mathematical function that returns the non-negative value whose square equals x. In the context of composite functions, it often serves as an outer function. Understanding its properties, such as its domain and range, is vital for determining how it can be combined with other functions to form a composite function like h(x).
Recommended video:
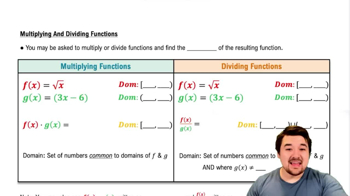
Multiplying & Dividing Functions

 5:56m
5:56mWatch next
Master Adding & Subtracting Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learning