Use the graph of f in the figure to evaluate the function or analyze the limit. <IMAGE>
f(−1)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution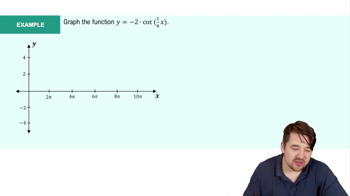


 6:47m
6:47mMaster Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning