Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 1.73
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionInverse sines and cosines Evaluate or simplify the following expressions without using a calculator.
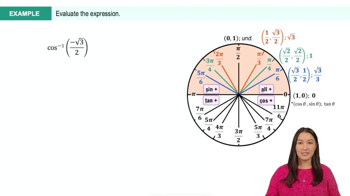
cos⁻¹ √3/2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
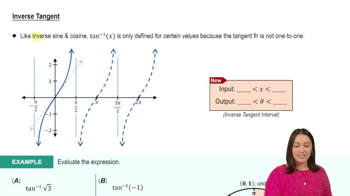
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Inverse trigonometric functions, such as sin⁻¹, cos⁻¹, and tan⁻¹, are used to find angles when given a ratio of sides in a right triangle. For example, cos⁻¹(x) returns the angle whose cosine is x. These functions are essential for solving problems where the angle is unknown, and they have specific ranges to ensure each output is unique.
Recommended video:

Derivatives of Other Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Unit Circle
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It is a fundamental tool in trigonometry, as it allows for the visualization of the sine and cosine values of angles. Understanding the unit circle helps in determining the angles corresponding to specific cosine and sine values, which is crucial for evaluating inverse trigonometric functions.
Recommended video:
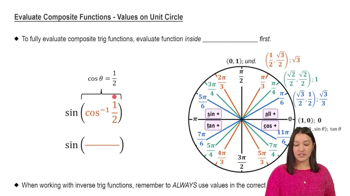
Evaluate Composite Functions - Values on Unit Circle
Cosine Values
The cosine function relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. For common angles, such as 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°, the cosine values are well-known. Recognizing that cos⁻¹(√3/2) corresponds to a specific angle on the unit circle is key to simplifying the expression without a calculator.
Recommended video:

Initial Value Problems
Related Videos
Related Practice