Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives
Intro to Extrema
Problem 4.R.2d
Textbook Question
Locating extrema Consider the graph of a function ƒ on the interval [-3, 3]. <IMAGE>
d. Give the approximate coordinates of the zero(s) of f.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
To find the zeros of the function f, we need to identify the points where the graph of the function intersects the x-axis. These points are where the function value is zero, i.e., f(x) = 0.
Examine the graph of the function on the interval [-3, 3]. Look for points where the curve crosses the x-axis. These crossings represent the zeros of the function.
Estimate the x-coordinates of these intersection points by observing the graph. Note that these are approximate values since we are visually inspecting the graph.
If the graph is not clear, consider using a more precise method such as numerical estimation or graphing software to find a more accurate approximation of the zeros.
Once you have identified the approximate x-coordinates, you can express the zeros as ordered pairs (x, 0), where x is the estimated x-coordinate of each zero.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Extrema
Extrema refer to the maximum and minimum values of a function within a given interval. These points are critical for understanding the behavior of the function, as they indicate where the function reaches its highest or lowest values. Identifying extrema often involves finding the derivative of the function and determining where it is zero or undefined.
Recommended video:
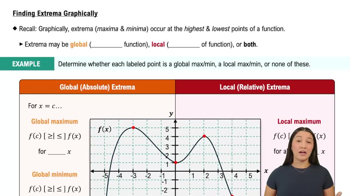
Finding Extrema Graphically
Zeros of a Function
The zeros of a function, also known as roots, are the values of the variable for which the function evaluates to zero. Finding these points is essential for understanding the function's behavior, as they indicate where the graph intersects the x-axis. Techniques for finding zeros include factoring, using the quadratic formula, or applying numerical methods.
Recommended video:
Guided course
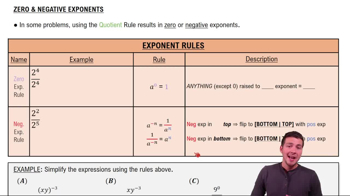
Zero and Negative Rules
Graphical Analysis
Graphical analysis involves examining the visual representation of a function to identify key features such as intercepts, extrema, and asymptotes. By analyzing the graph, one can gain insights into the function's behavior over a specified interval, making it easier to approximate coordinates of zeros and extrema without relying solely on algebraic methods.
Recommended video:
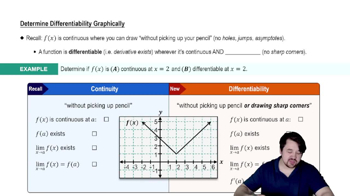
Determining Differentiability Graphically

 5:58m
5:58mWatch next
Master Finding Extrema Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning




