Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 1.R.75
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionInverse sines and cosines Evaluate or simplify the following expressions without using a calculator.
sin⁻¹ ( -1 )
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
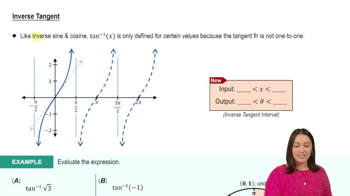
Inverse trigonometric functions, such as sin⁻¹ (arcsin) and cos⁻¹ (arccos), are used to find angles when the value of a sine or cosine is known. For example, sin⁻¹(x) gives the angle whose sine is x, with a principal range typically between -π/2 and π/2 for arcsin. Understanding these functions is crucial for evaluating expressions involving inverse trigonometric values.
Recommended video:

Derivatives of Other Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Range of Inverse Sine Function
The range of the inverse sine function, sin⁻¹(x), is limited to the interval [-π/2, π/2]. This means that when evaluating sin⁻¹(-1), we are looking for an angle within this range whose sine value is -1. Recognizing this range helps in determining the correct angle corresponding to the given sine value.
Recommended video:

Inverse Sine
Unit Circle
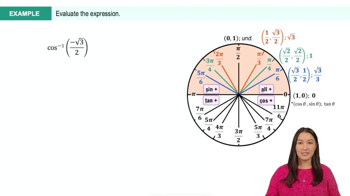
The unit circle is a fundamental concept in trigonometry that helps visualize the values of sine and cosine for various angles. It is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. The sine of an angle corresponds to the y-coordinate of the point on the unit circle, which aids in understanding why sin⁻¹(-1) equals -π/2, as this is the angle where the sine value reaches its minimum.
Recommended video:
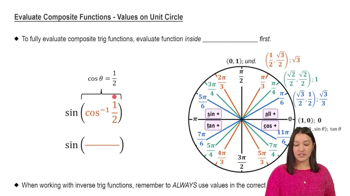
Evaluate Composite Functions - Values on Unit Circle
Related Videos
Related Practice