Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits
Problem 2.4.53b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDetermine whether the following statements are true and give an explanation or counterexample.
The line x=−1 is a vertical asymptote of the function f(x) =x^2 − 7x + 6 / x^2 − 1.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Vertical Asymptotes
A vertical asymptote occurs in a function when the function approaches infinity or negative infinity as the input approaches a certain value. This typically happens at values of x that make the denominator of a rational function equal to zero, provided that the numerator does not also equal zero at that point.
Recommended video:
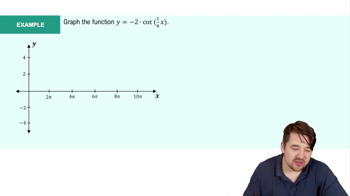
Introduction to Cotangent Graph Example 1
Rational Functions
A rational function is a function that can be expressed as the ratio of two polynomials. The general form is f(x) = P(x)/Q(x), where P and Q are polynomials. Understanding the behavior of rational functions, especially their asymptotic behavior, is crucial for analyzing their graphs and determining points of discontinuity.
Recommended video:
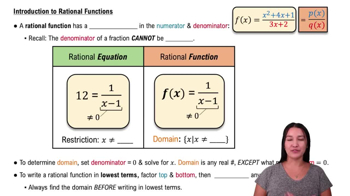
Intro to Rational Functions
Factoring Polynomials
Factoring polynomials involves rewriting a polynomial as a product of its factors, which can simplify the analysis of functions. For example, the function f(x) = (x^2 - 7x + 6)/(x^2 - 1) can be factored to identify points where the function is undefined, helping to determine the presence of vertical asymptotes.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Polynomial Functions

 6:47m
6:47mWatch next
Master Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning