Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Combining Functions
Problem 82c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionComposition of polynomials
Let ƒ be an nth-degree polynomial and let g be an mth-degree polynomial.
What is the degree of the following polynomials?
ƒ ⋅ f
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
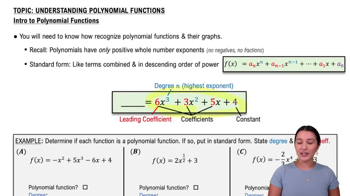
Degree of a Polynomial
The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial expression. For example, in the polynomial f(x) = 3x^4 + 2x^2 + 1, the degree is 4. The degree provides important information about the polynomial's behavior, including the number of roots and the end behavior of its graph.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Multiplication of Polynomials
When multiplying polynomials, the degree of the resulting polynomial is the sum of the degrees of the polynomials being multiplied. For instance, if f is an nth-degree polynomial and g is an mth-degree polynomial, then the degree of the product f ⋅ g is n + m. This principle is crucial for determining the degree of polynomial expressions resulting from operations.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Composition of Polynomials
The composition of polynomials involves substituting one polynomial into another. For example, if f(x) is a polynomial and g(x) is another, then the composition f(g(x)) results in a new polynomial. While the question focuses on multiplication, understanding composition helps clarify how polynomials interact, especially in more complex expressions.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Polynomial Functions

 5:56m
5:56mWatch next
Master Adding & Subtracting Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learning