Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits
Problem 2.23
Textbook Question
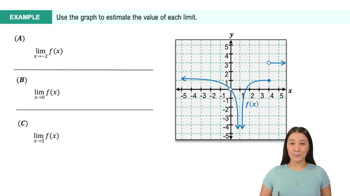
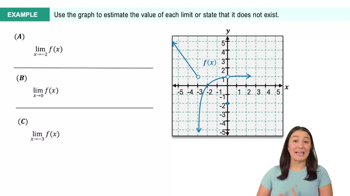
Textbook QuestionSketch a graph of f and use it to make a conjecture about the values of f(a), lim x→a^−f(x),lim x→a^+f(x), and lim x→a f(x) or state that they do not exist.
f(x) = x^2−25 / x−5; a=5
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Limits
Limits describe the behavior of a function as it approaches a specific point from either side. In this case, we analyze the limits as x approaches 5 from the left (lim x→5^−f(x)) and from the right (lim x→5^+f(x)). Understanding limits is crucial for determining the continuity and behavior of the function at that point.
Recommended video:

One-Sided Limits
Continuity
A function is continuous at a point if the limit as x approaches that point equals the function's value at that point. For the function f(x) = (x^2−25)/(x−5), we need to check if f(5) exists and if it matches the limits from both sides. If the function is not continuous at a, it may indicate a hole or vertical asymptote.
Recommended video:

Intro to Continuity
Graphing Rational Functions
Graphing rational functions involves identifying key features such as holes, vertical asymptotes, and intercepts. For f(x) = (x^2−25)/(x−5), we can simplify it to f(x) = x + 5 for x ≠ 5, which helps visualize the function's behavior around x = 5. This understanding aids in making conjectures about the function's values and limits.
Recommended video:

Graph of Sine and Cosine Function

 6:47m
6:47mWatch next
Master Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning