Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Common Functions
Problem 65e
Textbook Question
Textbook Question{Use of Tech} Height and time The height in feet of a baseball hit straight up from the ground with an initial velocity of 64 ft/s is given by h= ƒ(t) = 64t - 16t² where t is measured in seconds after the hit.
e. At what time is the ball at a height of 10 ft on the way down?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
8mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
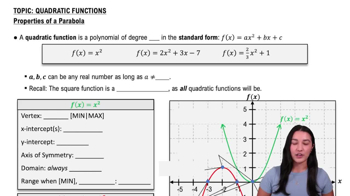
Quadratic Functions
The height function h(t) = 64t - 16t² is a quadratic function, which is a polynomial of degree two. Quadratic functions graph as parabolas and can model various physical phenomena, such as projectile motion. Understanding the properties of parabolas, including their vertex and intercepts, is essential for analyzing the height of the baseball over time.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Solving Quadratic Equations
To find the time when the baseball reaches a height of 10 ft, we need to solve the equation 64t - 16t² = 10. This involves rearranging the equation into standard form and applying methods such as factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. Mastery of these techniques is crucial for determining specific values of t in quadratic scenarios.
Recommended video:
Solving Logarithmic Equations
Projectile Motion
The scenario describes projectile motion, where an object is thrown vertically and affected by gravity. The height of the object over time can be modeled using a quadratic equation, where the initial velocity and gravitational acceleration influence the trajectory. Understanding the principles of projectile motion helps in interpreting the behavior of the baseball as it rises and falls.
Recommended video:

Derivatives Applied To Acceleration Example 2

 5:57m
5:57mWatch next
Master Graphs of Common Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice