Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Properties of Logarithms
Problem 77e
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDetermine whether the following statements are true and give an explanation or counterexample.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Natural Logarithm
The natural logarithm, denoted as ln, is the logarithm to the base e, where e is approximately 2.71828. It is a fundamental concept in calculus, particularly in relation to exponential functions. The natural logarithm has properties that make it useful for solving equations involving exponential growth or decay, and it is often used in integration and differentiation.
Recommended video:
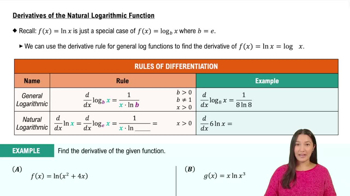
Derivative of the Natural Logarithmic Function
Exponential Functions
Exponential functions are mathematical functions of the form f(x) = a * e^(bx), where a and b are constants, and e is the base of the natural logarithm. These functions exhibit rapid growth or decay and are characterized by their constant percentage rate of change. Understanding exponential functions is crucial for analyzing growth models, compound interest, and natural phenomena.
Recommended video:
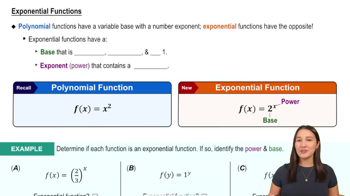
Exponential Functions
Equality of Functions
To determine if two expressions are equal, one must evaluate both sides under the same conditions. In calculus, this often involves substituting values or simplifying expressions. For the statement 2 = ln(2^e), one must understand how to manipulate logarithmic identities and evaluate the left and right sides to verify their equality or find a counterexample.
Recommended video:
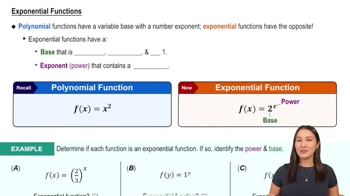
Exponential Functions







