Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
0. Functions
Common Functions
Problem 31
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionEvaluating trigonometric functions Without using a calculator, evaluate the following expressions or state that the quantity is undefined.
sec (5π/2)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and secant, relate angles to ratios of sides in right triangles. The secant function, specifically, is defined as the reciprocal of the cosine function. Understanding these functions is crucial for evaluating expressions involving angles, especially in the context of the unit circle.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Unit Circle
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It provides a geometric interpretation of trigonometric functions, where the x-coordinate represents the cosine and the y-coordinate represents the sine of an angle. Knowing how to locate angles on the unit circle helps in determining the values of trigonometric functions for various angles.
Recommended video:
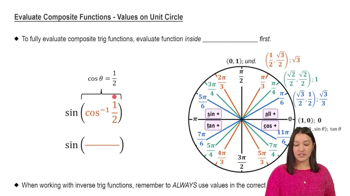
Evaluate Composite Functions - Values on Unit Circle
Angle Measurement and Periodicity
Angles can be measured in degrees or radians, with radians being the standard unit in calculus. The periodic nature of trigonometric functions means they repeat their values at regular intervals. For example, the secant function has a period of 2π, which is essential for evaluating angles like 5π/2, as it can be simplified to an equivalent angle within the standard range.
Recommended video:
Trig Values in Quadrants II, III, & IV Example 2

 5:57m
5:57mWatch next
Master Graphs of Common Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice