Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals3h 25m
0. Functions
Exponential & Logarithmic Equations
Problem 1.60
Textbook Question
Solving equations Solve the following equations.
5(ˣ³) = 29
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Start by isolating the term with the variable. Divide both sides of the equation by 5 to get x^3 = \frac{29}{5}.
Step 2: To solve for x, take the cube root of both sides of the equation. This will give you x = \sqrt[3]{\frac{29}{5}}.
Step 3: Simplify the expression if possible. In this case, \sqrt[3]{\frac{29}{5}} is already in its simplest form.
Step 4: Consider the properties of cube roots. Remember that the cube root of a number can be positive or negative, but since we are dealing with real numbers, we focus on the principal (positive) root.
Step 5: Verify your solution by substituting x back into the original equation to ensure that both sides are equal.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
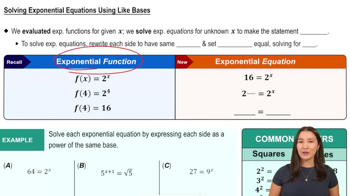
Exponential Equations
Exponential equations involve variables in the exponent, such as the equation 5(x³) = 29. To solve these equations, one typically isolates the exponential term and applies logarithmic functions to both sides, allowing for the extraction of the variable from the exponent.
Recommended video:
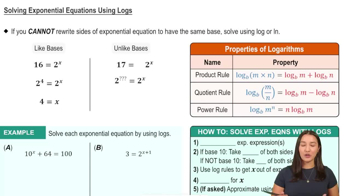
Solving Exponential Equations Using Logs
Logarithms
Logarithms are the inverse operations of exponentiation. They allow us to solve for the exponent in an equation. For example, if we have an equation in the form a^b = c, we can use logarithms to express b as log_a(c), which is essential for solving exponential equations.
Recommended video:

Logarithms Introduction
Algebraic Manipulation
Algebraic manipulation involves rearranging and simplifying equations to isolate the variable of interest. This includes operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as applying properties of equality to maintain balance in the equation while solving for the unknown.
Recommended video:

Determine Continuity Algebraically

 4:46m
4:46mWatch next
Master Solving Exponential Equations Using Like Bases with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice