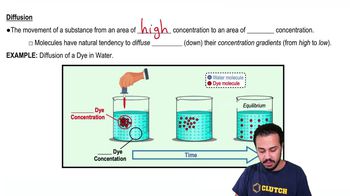
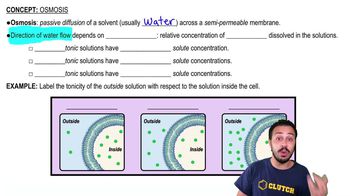
An artificial 'cell' consisting of an aqueous solution enclosed in a selectively permeable membrane is immersed in a beaker containing a different solution, the 'environment,' as shown in the accompanying diagram. The membrane is permeable to water and to the simple sugars glucose and fructose but impermeable to the disaccharide sucrose.
a. Draw solid arrows to indicate the net movement of solutes into and/or out of the cell.
b. Is the solution outside the cell isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic?
c. Draw a dashed arrow to show the net osmosis, if any.
d. Will the artificial cell become more flaccid, more turgid, or stay the same?
e. Eventually, will the two solutions have the same or different solute concentrations?