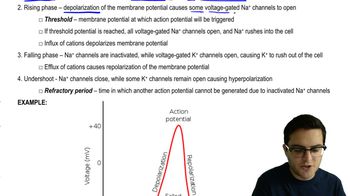
What happens when a resting neuron's membrane depolarizes?
a. There is a net diffusion of Na⁺ out of the cell
b. The equilibrium potential for K⁺ (Eₖ) becomes more positive
c. The neuron's membrane voltage becomes more positive
d. The cell's inside is more negative than the outside