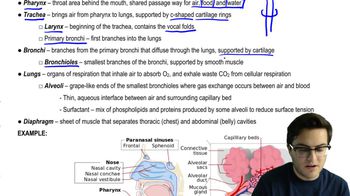
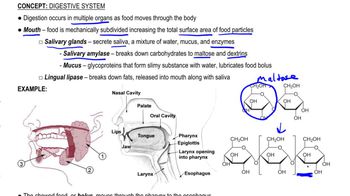
Fat digestion yields fatty acids and glycerol. Protein digestion yields amino acids. Both digestive processes
a. Occur inside cells in most animals
b. Add a water molecule to break bonds
c. Require a low pH resulting from HCl production
d. Consume ATP