Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, producing oxygen as a byproduct. It involves the absorption of light by chlorophyll and the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is crucial for the survival of most life forms on Earth as it provides oxygen and organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Pigments of Photosynthesis
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a group of photosynthetic bacteria that perform plantlike photosynthesis, releasing oxygen. They are significant contributors to the Earth's oxygen supply and are found in diverse environments, from oceans to freshwater systems. Cyanobacteria possess chlorophyll and use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, similar to plants.
Recommended video:
Chemoautotrophic Bacteria
Chemoautotrophic bacteria obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic substances, such as hydrogen sulfide or ammonia, rather than through photosynthesis. They do not release oxygen as a byproduct because their energy conversion process does not involve the splitting of water molecules. These bacteria play a vital role in nutrient cycling, particularly in environments where sunlight is scarce, such as deep-sea vents.
Recommended video:
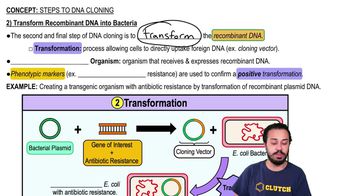
2) Transform Recombinant DNA into Bacteria

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance