Which of the following best demonstrates the unity among all organisms?
a. Emergent properties
b. Descent with modification
c. The structure and function of DNA
d. Natural selection
 Urry 11th Edition
Urry 11th Edition Ch. 1 - Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
Ch. 1 - Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Problem 6
Problem 6 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Which of the following best demonstrates the unity among all organisms?
a. Emergent properties
b. Descent with modification
c. The structure and function of DNA
d. Natural selection
A controlled experiment is one that
a. Proceeds slowly enough that a scientist can make careful records of the results.
b. Tests experimental and control groups in parallel.
c. Is repeated many times to make sure the results are accurate.
d. Keeps all variables constant.
Which of the following statements best distinguishes hypotheses from theories in science?
a. Theories are hypotheses that have been proved.
b. Hypotheses are guesses; theories are correct answers.
c. Hypotheses usually are relatively narrow in scope; theories have broad explanatory power.
d. Theories are proved true; hypotheses are often contradicted by experimental results.
Which sentence best describes the logic of scientific inquiry?
a. If I generate a testable hypothesis, tests and observations will support it.
b. If my prediction is correct, it will lead to a testable hypothesis.
c. If my observations are accurate, they will support my hypothesis.
d. If my hypothesis is correct, I can expect certain test results.
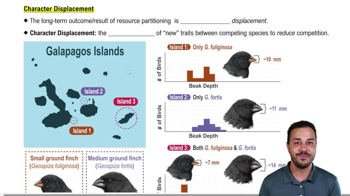
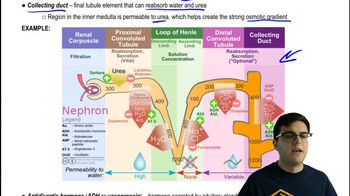
Draw a biological hierarchy similar to the one in Figure 1.3 but using a coral reef as the ecosystem, a fish as the organism, its stomach as the organ, and DNA as the molecule. Include all levels in the hierarchy.
<IMAGE>