Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
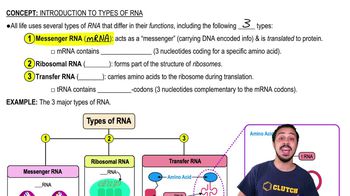
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a type of RNA molecule that plays a crucial role in the process of translation, where proteins are synthesized. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid to the ribosome, the cellular machinery that assembles proteins. The tRNA recognizes the corresponding codon on the messenger RNA (mRNA) through its anticodon region, ensuring that the correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Types of RNA
Anticodon and Codon Interaction
The anticodon is a sequence of three nucleotides on the tRNA that is complementary to a specific codon on the mRNA. This interaction is essential for the accurate translation of genetic information into proteins. When the tRNA's anticodon pairs with the mRNA's codon, it ensures that the correct amino acid is incorporated into the protein, maintaining the fidelity of protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
Interspecific Interactions
Role of Ribosomes in Protein Synthesis
Ribosomes are the cellular structures where protein synthesis occurs, facilitating the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain. They consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins, forming two subunits that come together during translation. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, allowing tRNA molecules to sequentially deliver amino acids, which are linked together to form proteins based on the genetic code.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance