Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
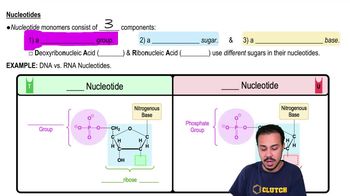
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose, while in RNA, it is ribose. The sequence of these nucleotides encodes genetic information, making them essential for the structure and function of both DNA and RNA.
Recommended video:
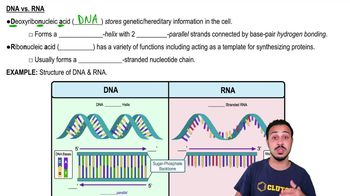
Differences between DNA and RNA
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) differ in several key aspects. DNA is typically double-stranded and contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA is usually single-stranded and contains ribose. Additionally, DNA uses thymine as one of its nitrogenous bases, whereas RNA uses uracil instead. These differences are crucial for their respective roles in genetic information storage and protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
Base Pairing
Base pairing refers to the specific hydrogen bonding between nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine, forming the double helix structure. In RNA, adenine pairs with uracil instead of thymine. This complementary base pairing is fundamental for processes like DNA replication and RNA transcription, ensuring accurate genetic information transfer.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance