Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a specific region and synthesizes a complementary RNA strand by pairing RNA nucleotides with the DNA template strand. This process is essential for gene expression, as it allows the information in DNA to be translated into proteins.
Recommended video:
1) Initiation of Transcription
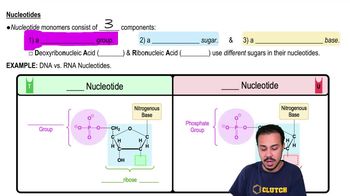
Nucleotide Base Pairing
Nucleotide base pairing refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). However, during transcription, uracil (U) replaces thymine in RNA, so adenine pairs with uracil. Understanding this pairing is crucial for determining the sequence of mRNA transcribed from a given DNA template.
Recommended video:
mRNA Sequence Directionality
The directionality of mRNA synthesis is important to understand, as mRNA is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction. This means that the RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing mRNA strand. Consequently, when transcribing from a DNA template, the mRNA sequence will be complementary to the DNA template strand and will reflect the reverse order of the DNA's coding strand.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance