Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in the production of gametes (sperm and eggs) with one copy of each chromosome. This process ensures genetic diversity through recombination and independent assortment, leading to gametes that are genetically distinct from one another and from the parent organism.
Recommended video:
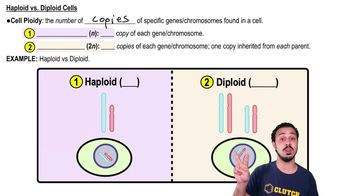
Haploidy
Haploidy refers to the condition of having a single set of chromosomes, which is characteristic of gametes in sexually reproducing organisms. In humans, sperm and eggs are haploid cells, containing one copy of each gene, which is crucial for maintaining the correct chromosome number upon fertilization when two haploid gametes combine to form a diploid zygote.
Recommended video:
Haploid vs. Diploid Cells
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is the diversity in gene frequencies within a population, which arises from processes such as mutation, recombination during meiosis, and independent assortment. This variation is essential for evolution and adaptation, as it provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, ensuring that offspring are not genetically identical to their parents or to each other.
Recommended video:
Sources of Genetic Variation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance