Types of Phosphorylation definitions Flashcards
Terms in this set (10)
ATP
A molecule that stores and transfers energy within cells, primarily produced during oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain of aerobic cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into ATP, water, and carbon dioxide, primarily through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Aerobic Respiration
Processes requiring oxygen to produce energy, typically yielding more ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration.
Anaerobic Respiration
Processes that occur without the presence of oxygen, often resulting in less ATP production compared to oxygen-dependent processes.
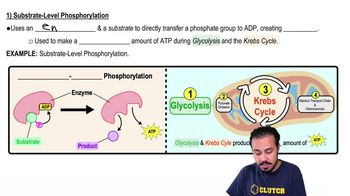
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
An enzyme-catalyzed process that directly transfers a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP, forming ATP, occurring during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
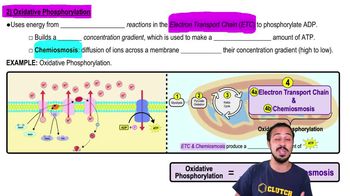
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP synthesis in the final steps of aerobic respiration using a hydrogen ion gradient and ATP synthase in the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons, creating a proton gradient to drive ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation.
Chemiosmosis
The movement of protons across a membrane, generating ATP via ATP synthase, driven by an electrochemical gradient established by the electron transport chain.
Pyruvate Oxidation
The conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, producing NADH and CO2, and linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration.
ATP Synthase
A complex enzyme that synthesizes ATP using a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane during oxidative phosphorylation.