The Steps of PCR quiz #1 Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (15)
What is the first step of the PCR cycle?
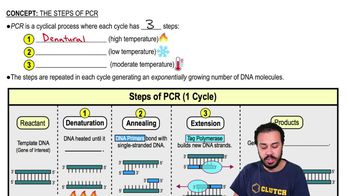
The first step of the PCR cycle is denaturation, where heat is used to denature the double-stranded DNA into single strands.
At what temperature does the denaturation step of PCR occur?
The denaturation step occurs at about 95 oC.
What is the role of Taq polymerase in PCR?
Taq polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase that can withstand high temperatures and is essential for synthesizing DNA during PCR.
Why is it important to use a thermostable polymerase like Taq polymerase in PCR?
It is important because Taq polymerase does not denature at the high temperatures used in PCR, allowing it to function throughout the cycle.
What happens to the DNA during the denaturation step of PCR?
The DNA is heated to break hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs, resulting in single-stranded DNA.
What is the second step of the PCR cycle?
The second step of the PCR cycle is annealing, where DNA primers bind to the single-stranded DNA.
At what temperature does the annealing step of PCR occur?
The annealing step occurs at about 55 degrees Celsius.
Why does Taq polymerase remain inactive during the annealing step?
Taq polymerase remains inactive because the temperature of 55 degrees Celsius is too low for its activity.
What is the third step of the PCR cycle?
The third step of the PCR cycle is extension, where Taq polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands.
At what temperature does the extension step of PCR occur?
The extension step occurs at about 72 oC.
What is the ideal temperature for Taq polymerase activity during PCR?
The ideal temperature for Taq polymerase activity is 72 oC.
What is the role of DNA primers in the PCR cycle?
DNA primers bind to the single-stranded DNA during the annealing step, providing a starting point for DNA synthesis.
How does Taq polymerase extend the DNA primers during the extension step?
Taq polymerase incorporates deoxyribonucleotides to extend the DNA primers, synthesizing new DNA strands.
What is the result of one complete PCR cycle?
One complete PCR cycle results in the replication of the original DNA, producing two identical copies.
Why is PCR considered a cyclic process?
PCR is cyclic because the products of one cycle serve as reactants for the next cycle, allowing exponential amplification of DNA.