The Steps of PCR definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (21)
PCR
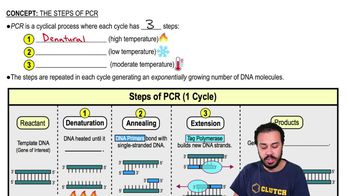
A cyclical process amplifying DNA by denaturing at high temperatures, annealing primers at low temperatures, and extending new strands with thermostable DNA polymerase at moderate temperatures.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
A technique to amplify DNA by cycling through denaturation, annealing, and extension steps, using heat-stable DNA polymerase to exponentially replicate the target sequence.
Denaturation
The process where high temperatures break hydrogen bonds in DNA, separating it into single strands, allowing each to serve as a template for replication.
Annealing
Annealing is the process in PCR where DNA primers bind to single-stranded DNA at cooler temperatures, enabling the next step of DNA synthesis.
Extension
The step in PCR where Taq polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the primers at moderate temperatures, typically around 72°C.
DNA
A molecule that carries genetic instructions in all living organisms, composed of two strands forming a double helix, with sequences of four types of nucleotides encoding biological information.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a pre-existing strand during DNA replication or PCR, functioning optimally at specific temperatures.
Taq Polymerase
A thermostable enzyme used in PCR to synthesize DNA at high temperatures, enabling the amplification of DNA sequences through repeated cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension.
Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA and RNA, each consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. They are essential for storing genetic information and energy transfer in cells.
DNA Nucleotides
The building blocks of DNA, each consisting of a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine.
Template DNA
The DNA strand that serves as a pattern for synthesizing a complementary strand during processes like PCR.
Pcr Primers
Short DNA sequences that bind to specific regions of the template DNA during PCR, enabling DNA polymerase to initiate replication.
Hydrogen Bonds
Attraction between a hydrogen atom in one molecule and an electronegative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) in another, crucial for DNA structure and protein folding.
Complementary Base Pairing
The process where specific nitrogenous bases (A-T and G-C) pair via hydrogen bonds, ensuring accurate DNA replication and transcription.
Single Stranded DNA
A DNA molecule consisting of a single strand of nucleotides, often used as a template in processes like PCR after denaturation separates the double-stranded DNA.
Double Stranded DNA
A molecule consisting of two complementary strands of nucleotides, held together by hydrogen bonds between paired bases, forming a double helix structure.
Thermostable Polymerase
A heat-resistant enzyme used in PCR to synthesize DNA at high temperatures, ensuring the DNA polymerase remains active during the denaturation step.
Gene Of Interest
A specific DNA sequence targeted for amplification or study in PCR, often chosen for its relevance to the research or diagnostic purpose.
5'
The end of a DNA or RNA strand with a free phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of the sugar molecule.
3'
The end of a DNA strand where the hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to the third carbon of the sugar ring, crucial for DNA synthesis directionality.
Celsius
A temperature scale where water freezes at 0oC and boils at 100oC, used to measure thermal conditions in biological processes like PCR.