The Lac Operon exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (24)
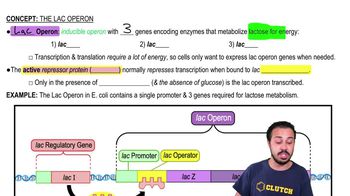
Lac Operon
An inducible operon in E. coli that includes genes for lactose metabolism.
What are the three genes in the lac operon?
lacZ, lacY, and lacA.
LacI
The repressor protein that binds to the operator to block transcription in the absence of lactose.
What happens to the lac operon in the absence of lactose?
The lacI repressor binds to the operator, blocking transcription.
Allolactose
A derivative of lactose that inactivates the lacI repressor, allowing transcription.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in the lac operon?
It initiates transcription of the lac operon genes when the repressor is inactive.
Inducible Operon
An operon that is normally off but can be turned on in the presence of a specific inducer.
What is the function of the lacZ gene?
Encodes β-galactosidase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose.
LacY
Encodes permease, which facilitates the entry of lactose into the cell.
What does the lacA gene encode?
Encodes transacetylase, an enzyme involved in lactose metabolism.
Operator
A DNA segment where the repressor binds to block transcription.
What triggers the inactivation of the lacI repressor?
The presence of allolactose.
What is the role of the lac operon in cellular metabolism?
It ensures energy efficiency by activating only when lactose is available and glucose is absent.
What happens to the lac operon in the presence of lactose?
Allolactose inactivates the repressor, allowing transcription of the operon.
Energy Efficiency
The concept that the lac operon is only activated when necessary to conserve energy.
What is the significance of glucose absence for the lac operon?
The lac operon is only activated when lactose is present and glucose is absent.
What is the function of β-galactosidase?
An enzyme that breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
What is the role of permease?
Facilitates the entry of lactose into the bacterial cell.
Repressor Protein
A protein that binds to the operator to prevent transcription.
What is the lac operon model organism?
E. coli.
Lactose
A sugar that can be metabolized by the enzymes encoded by the lac operon.
What is the function of transacetylase?
An enzyme involved in the metabolism of lactose.
Inducer
A molecule that initiates gene expression by inactivating a repressor.
What is the role of the lac promoter?
A DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds to start transcription of the lac operon.