The Biological Species Concept exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (28)
Biological Species Concept
Defines species based on reproductive isolation, preventing gene flow between populations.
What is reproductive isolation?
A barrier that prevents gene flow between species, ensuring they remain distinct.
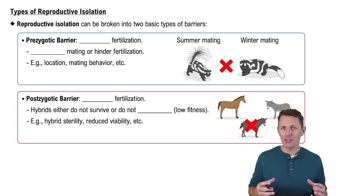
Prezygotic Barriers
Barriers that prevent mating or fertilization before the formation of a zygote.
Postzygotic Barriers
Barriers that occur after fertilization, reducing the viability or fertility of hybrids.
What is habitat isolation?
When populations live or breed in different habitats, preventing them from mating.
Temporal Isolation
When populations mate at different times of day or seasons, preventing interbreeding.
Behavioral Isolation
When differences in mating behaviors prevent populations from recognizing each other as potential mates.
Mechanical Isolation
When anatomical differences prevent successful mating between populations.
Gametic Isolation
When sperm and egg are biochemically incompatible, preventing fertilization.
What is hybrid sterility?
When hybrids are viable but cannot reproduce, preventing gene flow.
Reduced Hybrid Viability
Hybrids are less likely to survive compared to non-hybrids, reducing gene flow.
Hybrid Breakdown
First-generation hybrids are viable and fertile, but subsequent generations are weak or sterile.
What is an example of temporal isolation?
Eastern and western spotted skunks mate in different seasons, preventing interbreeding.
Example of mechanical isolation
Different species of damselflies have incompatible reproductive structures.
Example of gametic isolation
Arabidopsis thaliana pollen requires specific biochemical interactions to adhere and fertilize.
What is an example of reduced hybrid viability?
Hybrid offspring of different Physidula bird species are less likely to hatch.
Example of hybrid sterility
Mules, offspring of horses and donkeys, are sterile and cannot reproduce.
Example of hybrid breakdown
Second-generation hybrids of two cotton species are weak and sterile.
What is the significance of reproductive isolation in speciation?
Reproductive isolation is essential for the emergence of new species by preventing gene flow.
What are the two main categories of reproductive barriers?
Prezygotic barriers and postzygotic barriers.
What does prezygotic mean?
Before the formation of a zygote or fertilized egg.
What does postzygotic mean?
After the formation of a zygote or fertilized egg.
What is the role of gene flow in species differentiation?
Gene flow makes populations more similar; blocking it helps maintain species differences.
What is an example of habitat isolation?
Kaibob and Abirt squirrels are separated by the Grand Canyon, preventing interbreeding.
What is an example of behavioral isolation?
Southern and northern cricket frogs have different mating calls, preventing interbreeding.
What is the test for different species under the biological species concept?
Whether they are reproductively isolated and do not produce viable or fertile offspring.
What is the significance of hybrid sterility in reproductive isolation?
It prevents hybrids from reproducing, blocking gene flow between parent species.
What is the significance of hybrid breakdown in reproductive isolation?
It reduces the fitness of subsequent generations, preventing gene flow.