Test Crosses exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (25)
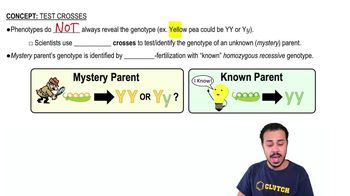
Test Cross
A method used to determine the genotype of an organism with a dominant phenotype by crossing it with a homozygous recessive organism.
What is the purpose of a test cross?
To determine the genotype of an organism with a dominant phenotype.
Homozygous Dominant
An organism with two dominant alleles for a trait (e.g., YY).
Heterozygous
An organism with one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait (e.g., Yy).
What does it mean if all offspring display the dominant phenotype in a test cross?
The mystery parent is homozygous dominant.
Homozygous Recessive
An organism with two recessive alleles for a trait (e.g., yy).
What does a mix of phenotypes in the offspring indicate in a test cross?
The mystery parent is heterozygous.
Phenotype
The observable traits of an organism.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
What are the three steps to performing a test cross?
1. Cross the mystery parent with a homozygous recessive parent. 2. Analyze the offspring phenotypes. 3. Make a conclusion about the mystery parent's genotype.
Dominant Allele
An allele that expresses its phenotype even in the presence of a recessive allele.
Recessive Allele
An allele that only expresses its phenotype when paired with another recessive allele.
What is the genotype of a yellow pea plant if all offspring are yellow in a test cross?
Homozygous dominant (YY).
What is the genotype of a yellow pea plant if the offspring are 50% yellow and 50% green in a test cross?
Heterozygous (Yy).
Cross Fertilization
The process of fertilizing one plant with the pollen from another plant.
What does a 100% dominant phenotype in offspring suggest about the mystery parent's genotype?
The mystery parent is homozygous dominant.
What does a 50% dominant and 50% recessive phenotype in offspring suggest about the mystery parent's genotype?
The mystery parent is heterozygous.
Allele
A variant form of a gene.
What is the role of a homozygous recessive parent in a test cross?
To provide a known genotype for comparison.
Why can't phenotype alone determine genotype?
Because a dominant phenotype can result from either a homozygous dominant or heterozygous genotype.
What does a test cross reveal about genetic inheritance?
It helps understand the role of alleles in determining traits.
Why is a homozygous recessive parent used in a test cross?
Because its genotype is known and it can reveal the genotype of the mystery parent.
What is the significance of analyzing offspring phenotypes in a test cross?
It helps determine the genotype of the mystery parent.
What does a dominant phenotype indicate about an organism's alleles?
The organism has at least one dominant allele.
What is the genotype of a green pea plant?
Homozygous recessive (yy).