Steps to DNA Cloning exam Flashcards
 Back
BackSteps to DNA Cloning exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
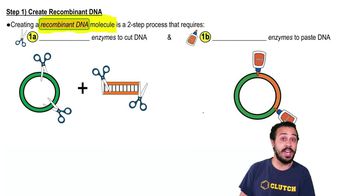
- Recombinant DNAA single DNA molecule that contains DNA from two different sources.
- What is the first step in DNA cloning?Creating the recombinant DNA molecule.
- Restriction EnzymesEnzymes that cut DNA at specific restriction sites, producing sticky ends.
- What is the role of DNA ligase in DNA cloning?It covalently joins the DNA fragments, acting like glue.
- TransformationThe process by which bacteria uptake recombinant DNA from their environment.
- What are sticky ends?Single-stranded DNA overhangs produced by restriction enzyme cuts.
- Transgenic OrganismAn organism that has received and expresses recombinant DNA from a different species.
- What is the purpose of using phenotypic markers in DNA cloning?To confirm a positive transformation, such as antibiotic resistance.
- Cloning VectorA DNA molecule used to carry foreign genetic material into a host cell.
- What is the second step in DNA cloning?Transforming the recombinant DNA into bacteria.
- Insulin ProductionA medical application of DNA cloning where transgenic bacteria produce human insulin.
- What is a restriction site?A specific DNA sequence where a restriction enzyme binds and cuts the DNA.
- DNA CloningA process involving creating recombinant DNA and transforming it into bacteria.
- What is the significance of sticky ends in DNA cloning?They allow complementary base pairing, facilitating the ligation of DNA fragments.
- Antibiotic ResistanceA phenotypic marker used to confirm successful transformation in bacteria.
- What is the role of a bacterial plasmid in DNA cloning?It serves as a vector to carry the gene of interest into the host cell.
- Gene of InterestA specific gene that is inserted into a plasmid for cloning purposes.
- What does the term 'ligation' refer to in DNA cloning?The process of joining DNA fragments together using DNA ligase.
- Therapeutic ProteinsProteins produced through DNA cloning for medical treatments, such as insulin.
- What is the purpose of creating recombinant DNA?To combine DNA from different sources for cloning and expression in host cells.
- E. ColiA common bacterial host used in DNA cloning to express recombinant genes.
- What is the outcome of successful DNA transformation?The bacteria express the foreign gene, producing the desired protein.
- Molecular ScissorsA metaphor for restriction enzymes that cut DNA at specific sites.
- What is the function of a cloning vector?To introduce foreign DNA into a host cell for replication and expression.
- DiabetesA condition treated with insulin produced by transgenic bacteria through DNA cloning.
- What is the significance of the transformation step in DNA cloning?It allows the recombinant DNA to be taken up by bacteria, enabling gene expression.
- Sticky EndsOverhanging sequences of single-stranded DNA created by restriction enzyme cuts.
- What is the role of restriction enzymes in creating recombinant DNA?They cut DNA at specific sites to create fragments with sticky ends for ligation.
- DNA LigaseAn enzyme that joins DNA fragments by forming covalent bonds.