Steps of Translation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (18)
Translation
The process where ribosomes synthesize proteins by decoding mRNA into a polypeptide chain, involving initiation, elongation, and termination steps.
Initiation
The initial phase of translation where the small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA and tRNA, followed by the large subunit, and the start codon AUG initiates protein synthesis.
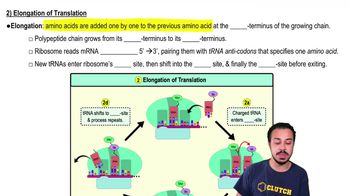
Elongation
The process in translation where amino acids are sequentially added to a growing polypeptide chain, extending it from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
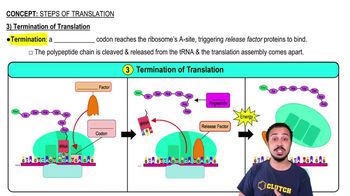
Termination
The final step of translation where a release factor binds to the stop codon, causing the ribosome to disassemble and release the newly synthesized polypeptide.
Ribosomal Subunit
A component of the ribosome, either large or small, that assembles with mRNA and tRNA to facilitate protein synthesis during translation.
Ribosome
A molecular machine that synthesizes proteins by translating messenger RNA sequences into polypeptide chains, using tRNA to match codons with corresponding amino acids.
mRNA
A molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it specifies the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression.
tRNA
A molecule that carries specific amino acids to the ribosome, matching its anticodon with mRNA codons to ensure correct protein synthesis during translation.
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or a start/stop signal during protein synthesis.
Start Codon
The codon AUG on mRNA that signals the ribosome to begin translation, coding for the amino acid methionine.
Aug
A codon in mRNA that signals the start of translation and specifies the amino acid methionine (MET).
Met
The amino acid methionine, abbreviated as Met, is specified by the start codon AUG and initiates protein synthesis during translation.
Polypeptide Chain
A sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, forming the primary structure of a protein, synthesized during translation from mRNA.
Initiation Factors
Proteins that assist in the assembly of the ribosome on mRNA and the binding of the first tRNA during the initiation phase of translation.
Anticodon
A sequence of three nucleotides in tRNA that pairs with a complementary codon in mRNA during protein synthesis.
Discharged tRNA
A tRNA molecule that has transferred its amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain and exits the ribosome through the E site.
Release Factor
A protein that binds to the stop codon in the ribosome's A site, triggering the release of the newly synthesized polypeptide, mRNA, and ribosomal subunits during translation termination.
Stop Codon
A nucleotide triplet in mRNA that signals the end of protein synthesis by binding a release factor instead of a tRNA, causing the ribosome to disassemble and release the newly formed polypeptide.